Internal Audit refers to an independent, objective assurance and consulting activity designed to add value and improve an organization's operations. It is conducted by internal auditors who are employees of the organization but are independent of the areas they audit. The primary purpose of internal audit is to evaluate and enhance the effectiveness of an organization's internal controls, risk management, and governance processes.
Applicability of Internal Audit
Internal Audit is mandatory for the following specified companies: -
- Every listed company;
- Every unlisted public company satisfying any of the following condition;
- Paid up share capital of INR 50 Crore or more during the preceding Financial Year; or
- Turnover of INR 200 Crore or more during the preceding Financial Year; or
- Outstanding loans/ borrowings from banks/ public financial institutions exceeding INR 100 Crores or more at any point of time during the preceding Financial Year; or
- Outstanding deposits of INR 25 Crores or more at any point of time during the preceding Financial Year.
- Every Private Company satisfying any of the following condition;
- Turnover of INR 200 Crore or more during the preceding Financial Year; or
- Outstanding loans/ borrowings from banks/ public financial institutions exceeding INR 100 Crores or more at any point of time during the preceding Financial Year.
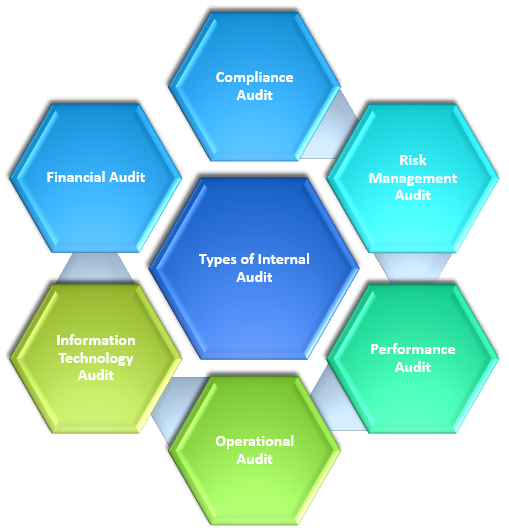
Types of Internal Audit
Organizations can perform various types of internal audits based on needs and objectives. Here are some common types of internal audit:
- Financial audit: Audit examines financial processes, controls, and reporting to ensure accuracy, compliance, and reliability of information.
For Example: A financial audit may involve examining financial statements, conducting tests of internal controls, and verifying the accuracy of financial data, such as revenue, expenses, and assets.
- Operational Audit: Operational audit assesses organizational efficiency, effectiveness, and optimization of activities, systems, and procedures.
For Example: An operational audit could involve analyzing manufacturing processes, supply chain management, sales operations, or customer service procedures to identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, or areas where best practices can be implemented.
- Compliance Audit: Compliance audit evaluates an organization's adherence to laws, regulations, industry standards, and policies.
For Example: A compliance audit may involve evaluating the organization's adherence to labor laws, environmental regulations, data protection regulations, or internal policies related to ethical conduct.
- Information Technology Audit: IT audit evaluates an organization's infrastructure, systems, and controls, assessing security measures, data integrity, governance, and alignment with business objectives.
For Example: An IT audit might involve reviewing the organization's data backup processes, network security measures, user access controls, and system change management procedures.
- Risk Management Audit: To evaluate the effectiveness of an organization's risk management processes.
For Example: Assessing the identification and assessment of risks, evaluating risk mitigation strategies, reviewing risk monitoring and reporting mechanisms, and ensuring alignment with risk appetite and tolerance levels.
- Performance Audit: Performance audit assesses organizational goals and objectives, evaluating program effectiveness, resource utilization, and making recommendations for improvement, analyzing key indicators.
For Example: Evaluating the performance of a specific department, reviewing the implementation of a new initiative, assessing the effectiveness of a training program, or evaluating the outcomes of a project.
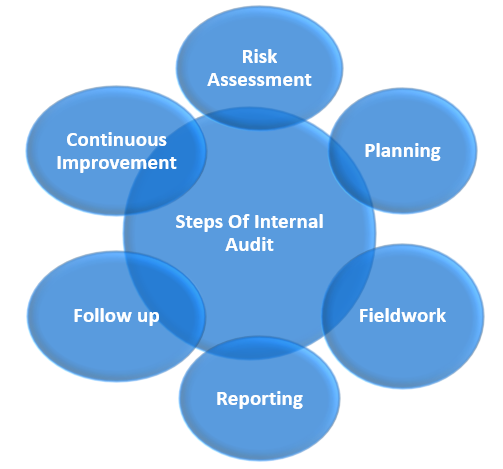
Steps of Internal Audit
Internal audit involves key components for evaluating and improving an organization's internal controls, risk management, and operational effectiveness.
Here are the Primary parts of Internal Audit-
- Risk Assessment: Internal audit assesses organization's risks, identifying potential threats, evaluating significance, and prioritizing them based on impact on objectives.
- Planning: Internal auditors create a strategic plan to address identified risks, determining scope, objectives, resource allocation, and timelines.
- Fieldwork: Fieldwork phase involves internal auditors gathering data, analyzing processes, and conducting interviews to assess internal controls, identify gaps, and ensure compliance with laws and regulations.
- Reporting: Internal auditors create detailed reports after fieldwork, sharing findings, observations, and recommendations for informed decision-making and improvement initiatives.
- Follow up: Internal audit involves monitoring recommendations implementation, assessing progress, and ensuring appropriate execution of actions to achieve desired improvements and address identified weaknesses.
- Continuous Improvement: Internal audit functions continuously improve processes and methodologies, providing valuable insights and assurance to organizations.
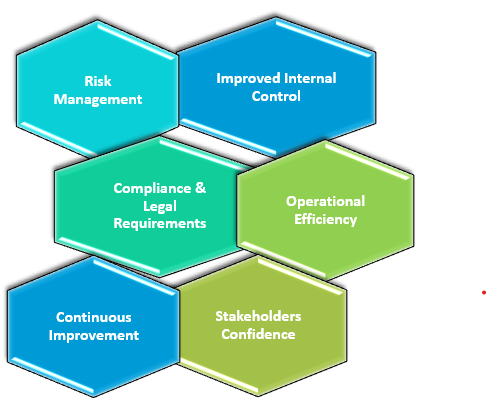
Benefits for an Organization
Internal audit offers numerous benefits to organizations, contributing to their overall success and effectiveness.
Internal audit benefits organizations through:
- Risk Management: Internal audit assesses and evaluates risks to achieve organizational objectives, providing insights and recommendations for mitigating them, enabling proactive risk management and asset protection.
- Improved Internal Control: Internal audit assesses controls' effectiveness, identifying weaknesses, and providing recommendations to strengthen them for asset safeguarding, financial reporting, and compliance.
- Compliance & Legal Requirements: Internal auditors evaluate an organization's compliance with laws, regulations, and policies, identifying non-compliance and potential legal risks, promoting ethical conduct and good governance.
- Operational Efficiency: Internal audit evaluates operational processes, identifying opportunities for improvement, recommending cost-saving measures, waste elimination, and resource optimization.
- Continuous Improvement: Internal audit functions promote continuous improvement, monitoring implementation and assessing progress in addressing weaknesses, contributing to organizational growth and development.
- Stakeholder Confidence: Internal audit function boosts stakeholder confidence by ensuring robust controls, risk management, and ethical behavior, leading to improved relationships and reputation.