Overview of Company Incorporation:
Company incorporation refers to the process of legally forming a business entity that is distinct from its owners. In India, this is primarily governed by the Companies Act, 2013, along with various rules and regulations prescribed by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA).
Types of Companies:
India offers various types of business structures, including:-
- Private Limited Companies,
- Public Limited Companies,
- and One-Person Companies (OPCs).
Each type has its own set of requirements, benefits, and limitations, catering to different business needs and objectives.
Why Incorporate a Company in India?
Incorporating a company in India offers numerous benefits and opportunities for entrepreneurs, businesses, and investors. Some of the key reasons why individuals and entities choose to incorporate a company in India include:
-
Limited Liability Protection: One of the primary reasons for incorporating a company is to benefit from limited liability protection. Shareholders' liability is limited to the extent of their investment in the company, which means personal assets are generally protected from business liabilities and debts.
-
Legal Recognition and Credibility: A registered company in India enjoys legal recognition as a separate legal entity distinct from its owners. This provides credibility and trustworthiness in dealings with customers, suppliers, financial institutions, and other stakeholders.
-
Access to Funding:( LLP) A registered company can access various sources of funding, including equity investments, loans, and venture capital. This facilitates business expansion, investment in infrastructure, research and development, and other growth initiatives.
-
Tax Benefits:Companies in India are subject to corporate tax rates, which may be more favorable compared to individual tax rates. Additionally, certain tax incentives and exemptions are available to eligible companies, encouraging investment in specific sectors or regions.
-
Ease of Doing Business: Despite bureaucratic challenges, India has made significant strides in improving its business environment through initiatives such as the introduction of online filing systems, streamlined procedures, and regulatory reforms aimed at facilitating ease of doing business.
-
Global Expansion: Incorporating a company in India provides a platform for domestic and international expansion. With its large consumer base, growing middle class, and diverse market opportunities, India serves as an attractive destination for businesses seeking to establish a presence in the Asia-Pacific region.
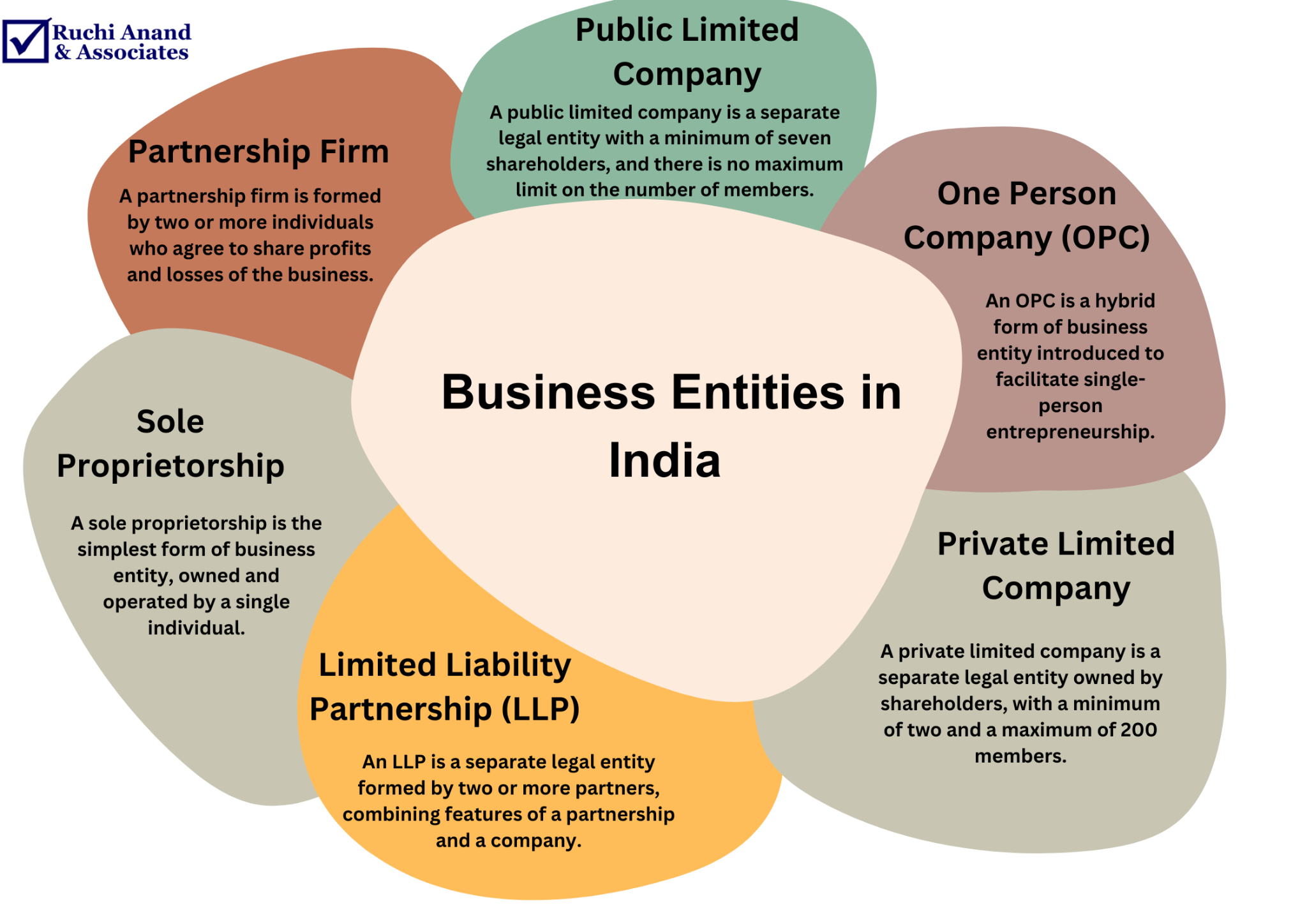
What Are the Types of Business Entities in India?
In India, various types of business entities can be established, each with its own legal structure, ownership, liability, and compliance requirements. The most common types of business entities in India include:
-
Sole Proprietorship:
- A sole proprietorship is the simplest form of business entity, owned and operated by a single individual.
- The owner has unlimited liability, meaning they are personally responsible for all debts and obligations of the business.
- No formal registration is required, but the proprietor may need to obtain licenses or permits depending on the nature of the business.
-
Partnership Firm:
- A partnership firm is formed by two or more individuals who agree to share profits and losses of the business.
- Partnerships can be registered or unregistered, but registration offers legal recognition and certain advantages.
- Partners have unlimited liability, and the firm is taxed as per the individual income tax rates of the partners.
-
Limited Liability Partnership (LLP):
- An LLP is a separate legal entity formed by two or more partners, combining features of a partnership and a company.
- Partners have limited liability, meaning their personal assets are protected from business debts and liabilities.
- LLPs are governed by the Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008, and require registration with the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA).
-
Private Limited Company:
- A private limited company is a separate legal entity owned by shareholders, with a minimum of two and a maximum of 200 members.
- Shareholders have limited liability, and the company's liability is limited to its assets.
- Private limited companies are governed by the Companies Act, 2013, and require registration with the Registrar of Companies (ROC).
-
Public Limited Company:
- A public limited company is a separate legal entity with a minimum of seven shareholders, and there is no maximum limit on the number of members.
- Shares of a public limited company can be traded publicly on stock exchanges.
- Public limited companies are subject to stricter regulatory compliance requirements compared to private limited companies.
-
One Person Company (OPC):
- An OPC is a hybrid form of business entity introduced to facilitate single-person entrepreneurship.
- It allows a single individual to establish a company with limited liability, similar to a private limited company.
- OPCs are governed by the Companies Act, 2013, and require nomination of a nominee director.
-
Producer Company:
- A producer company is formed by primary producers engaged in activities related to agriculture, horticulture, animal husbandry, or any other primary produce.
- It is registered as a company under the Companies Act, 2013, and provides benefits to its members in terms of better bargaining power, access to credit, and marketing opportunities.
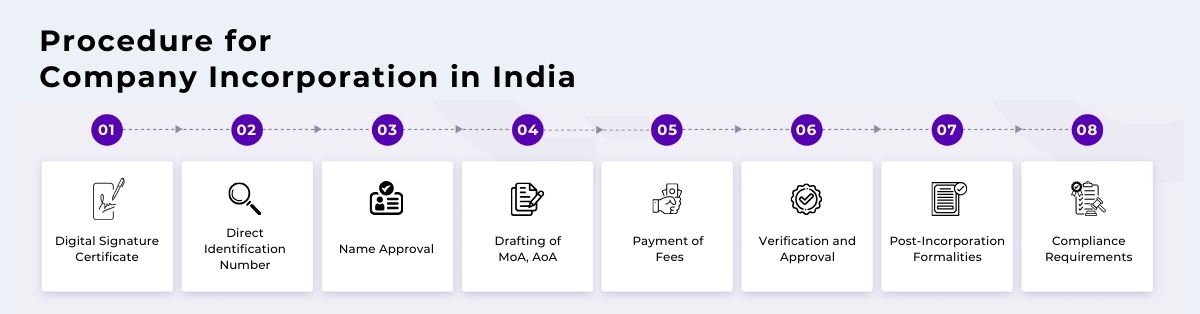
What Is The Procedure for Company Incorporation in India?
The procedure for company incorporation in India involves several steps and compliances with the relevant regulatory authorities. Here's a detailed overview of the process:
- Obtain Digital Signature Certificate (DSC):
- The first step is to obtain Digital Signature Certificates (DSCs) for all proposed directors of the company. This is necessary for digitally signing documents during the incorporation process.
Director Identification Number (DIN) Application:
- Directors must apply for Director Identification Numbers (DINs) from the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA). DIN is a unique identification number required for directors to incorporate a company.
Name Reservation and Approval:
- Choose a unique name for the company and apply for name reservation through the MCA's portal. The proposed name should comply with the naming guidelines prescribed under the Companies Act, 2013.
- Once the name is approved, it remains reserved for 20 days from the date of approval.
Draft the MoA and AoA, which outline the company's objectives, structure, and internal regulations. These documents must be prepared in accordance with the format prescribed under the Companies Act, 2013.
Filing Incorporation Documents:
- Memorandum of Association (MoA)
- Articles of Association (AoA)
- Form SPICe (Simplified Proforma for Incorporating Company Electronically) - INC-32
- Form INC-33 (e-MoA) and Form INC-34 (e-AoA) if applicable2
- Declaration by directors and subscribers
- Address proof, identity proof, and photographs of directors and subscribers
Payment of Fees:
- Pay the requisite incorporation fees online as per the Companies (Registration Offices and Fees) Rules, 2014.
Verification and Approval:
- The ROC verifies the submitted documents and ensures compliance with the provisions of the Companies Act, 2013.
- Upon verification and approval, the ROC issues a Certificate of Incorporation, confirming the formation of the company.
Post-Incorporation Formalities:
- Obtain Permanent Account Number (PAN) and Tax Deduction and Collection Account Number (TAN) from the Income Tax Department.
- Open a bank account in the name of the company and deposit the initial share capital.
- Register for Goods and Services Tax (GST) if applicable.
Compliance Requirements:
- Fulfill ongoing compliance requirements, including statutory filings, appointment of auditors, conducting board meetings, and maintaining statutory registers.
Step-By-Step Process to Company incorporation in India.
The step-by-step process for company incorporation in India involves several sequential steps. Here's a detailed breakdown of each step:
-
Obtain Digital Signature Certificate (DSC):
The first step is to obtain Digital Signature Certificates (DSCs) for all proposed directors of the company. This is necessary for digitally signing documents during the incorporation process.
-
Apply for Director Identification Number (DIN):
Directors must apply for Director Identification Numbers (DINs) from the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA). DIN is a unique identification number required for directors to incorporate a company.
-
Name Approval:
Choose a unique name for the company and apply for name approval through the MCA's RUN (Reserve Unique Name) web service. The proposed name should comply with the naming guidelines prescribed under the Companies Act, 2013.
-
Drafting of Memorandum of Association (MoA) and Articles of Association (AoA):
Draft the MoA and AoA, which define the constitution, objectives, and internal regulations of the company. These documents must be prepared in accordance with the format prescribed under the Companies Act, 2013.
-
Incorporation Application Submission:
Prepare and submit the following documents to the Registrar of Companies (ROC) electronically:
- Memorandum of Association (MoA)
- Articles of Association (AoA)
- Form SPICe (Simplified Proforma for Incorporating Company Electronically) - INC-32
- Form INC-33 (e-MoA) and Form INC-34 (e-AoA) if applicable
- Declaration by directors and subscribers
- Address proof, identity proof, and photographs of directors and subscribers
-
Payment of Fees:
Pay the requisite incorporation fees online as per the Companies (Registration Offices and Fees) Rules, 2014.
-
Verification of Documents:
The ROC verifies the submitted documents and ensures compliance with the provisions of the Companies Act, 2013.
-
Certificate of Incorporation:
Upon verification of documents and payment of fees, the ROC issues a Certificate of Incorporation. This certificate serves as conclusive evidence of the formation of the company.
-
PAN and TAN Application:
Apply for Permanent Account Number (PAN) and Tax Deduction and Collection Account Number (TAN) with the Income Tax Department.
-
Bank Account Opening:
Open a bank account in the name of the company and deposit the initial share capital.
-
GST Registration:
Register for Goods and Services Tax (GST) if the company's turnover exceeds the prescribed threshold.
-
Compliance Requirements:
Fulfill ongoing compliance requirements, including statutory filings, appointment of auditors, conducting board meetings, and maintaining statutory registers.
FAQs on Company incorporation in India?
How Ruchi Anand & Associates Helps in Company incorporation in India.
Ruchi Anand & Associates is a professional services firm that offers comprehensive assistance and expertise in company incorporation services in India. Here's how Ruchi Anand & Associates helps in company incorporation:
- Expert Guidance and Consultation:
Ruchi Anand & Associates provides expert guidance and consultation to clients on the various legal structures available for company incorporation in India, helping them choose the most suitable option based on their business objectives and requirements.
- Pre-Incorporation Advisory Services:
The firm offers pre-incorporation advisory services, including assistance in name reservation, preparation of Memorandum of Association (MoA) and Articles of Association (AoA), and compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Document Preparation and Filing:
Ruchi Anand & Associates assists clients in the preparation and filing of incorporation documents, including Form SPICe (Simplified Proforma for Incorporating Company Electronically) and other necessary forms with the Registrar of Companies (ROC).
- Digital Signature Certificates (DSC) and Director Identification Number (DIN):
The firm facilitates the procurement of Digital Signature Certificates (DSC) for directors and the application for Director Identification Numbers (DIN) as required for company incorporation.
- Name Approval Process:
Ruchi Anand & Associates helps clients in the name approval process by conducting a thorough check for name availability, ensuring compliance with the naming guidelines, and submitting the name reservation application through the MCA's portal.
We’re Always Available
You can contact us on our given contact details. You can even chat with our experts by entering your email, phone number and request a callback. Our experts will contact you and clear all your queries.
If you have any questions to wish to know more about “Company registration in India”, kindly Contact us.