Data Security Audit
Data Security Audit
A Data Security Audit is a systematic evaluation and assessment of an organization's data security practices and measures to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive information. It involves a comprehensive review of the organization's data protection policies, procedures, controls, and technical safeguards to identify potential vulnerabilities and risks.
The primary objective of a data security audit is to determine the effectiveness of an organization's data security controls and identify any gaps or weaknesses that could expose sensitive data to unauthorized access, alteration, or destruction. The audit helps ensure that data is adequately protected and that the organization is complying with relevant regulations, industry standards, and internal policies.
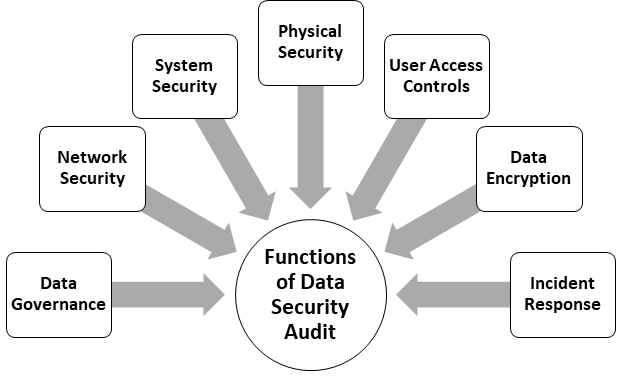
Functions of Data Security Audit
Data security audit examines organization's practices, including:
- Data governance: This involves assessing the organization's data management processes, including data classification, access controls, data retention, and disposal practices.
- Network security: The audit evaluates the organization's network infrastructure, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and other security measures to ensure that they are properly configured and updated.
- Physical security: This includes reviewing physical access controls, such as locks, surveillance systems, and data centre security measures, to protect against unauthorized physical access to sensitive data.
- System Security: The audit assesses the security of servers, databases, and other IT systems to ensure that they are protected against potential vulnerabilities and threats.
- User access controls: The audit examines user authentication mechanisms, password policies, and user access management processes to verify that access to sensitive data is appropriately restricted.
- Data encryption: The audit reviews the organization's encryption practices to ensure that sensitive data is properly encrypted during storage and transmission.
- Incident response: The audit assesses the organization's incident response procedures to determine its ability to detect, respond to, and recover from security incidents or breaches.
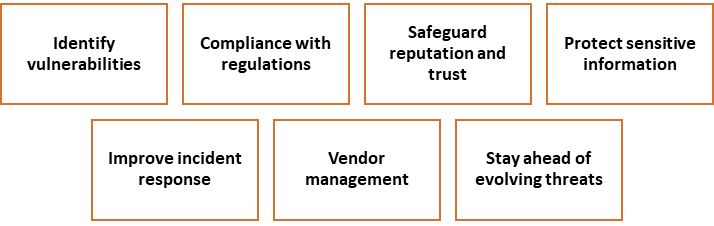
Need of Data Security Audit
- Identify vulnerabilities: Data security audits detect vulnerabilities, weaknesses, and potential security gaps in an organization's practices and infrastructure.
- Compliance with regulations: Data security audits ensure industry compliance with strict regulations, preventing legal and financial consequences for organizations.
- Safeguard reputation and trust: Regular data security audits protect an organization's reputation and trust by demonstrating commitment to data protection.
- Protect sensitive information: Data security audits safeguard sensitive information by examining processes, access controls, and encryption practices to prevent unauthorized access, alteration, or disclosure.
- Improve incident response: Data security audits assess organizations' incident response procedures, identifying weaknesses and implementing recommended improvements for effective mitigation and management of security breaches.
- Vendor management: Data security audits are crucial for managing third-party vendors, evaluating their security measures and practices to ensure compliance with data security standards.
- Stay ahead of evolving threats: Data security audits help organizations stay updated on emerging threats and technologies, ensuring adequate measures to protect against evolving threats.
Need of Data Security Audit
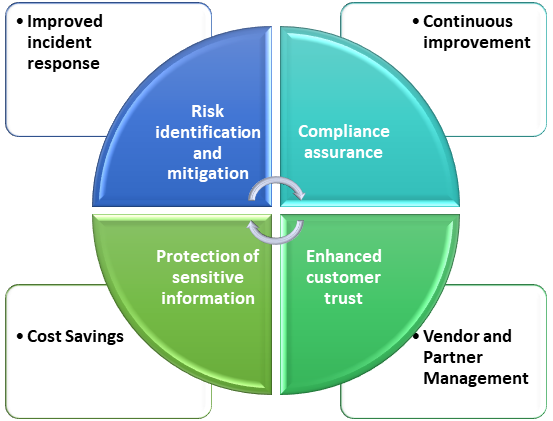
Benefits for an Organization
Data security audits provide numerous benefits to organizations:
- Risk identification and mitigation: Data security audits assess risks, vulnerabilities, and weaknesses in an organization's infrastructure, enabling proactive risk mitigation and enhanced security posture.
- Compliance assurance: Data security audits ensure organizations meet strict regulations, preventing penalties, legal issues, and reputational damage in industries.
- Protection of sensitive information: Data security audits safeguard sensitive information by identifying gaps, implementing safeguards, and preventing unauthorized access or breaches, ensuring organizational value.
- Enhanced customer trust: Conducting data security audits builds customer trust, strengthens relationships, and differentiates organizations from competitors by ensuring secure handling and protection.
- Improved incident response: Data security audits assess organizations' incident response capabilities, identifying weaknesses and gaps, enhancing detection, response, and recovery processes for reduced downtime and breach impact.
- Continuous improvement: Data security audits are ongoing processes for organizations to assess, improve, and adapt to new threats, technologies, and regulatory changes.
- Cost Savings: Regular data security audits reduce financial losses and risks associated with data breaches and security incidents.
- Vendor and Partner Management: Organizations collaborate with third-party vendors or partners, requiring data security audits to evaluate practices, reducing risk of breaches in the vendor ecosystem.